Crypto Custody Explained: Navigating Self-Custody and Third-Party Services
Summary
Introduction: Crypto Custody Explained
In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrencies, understanding how to securely store and manage your digital assets is paramount. The concept of “crypto custody” refers to the methods and services used to protect and control access to cryptocurrencies. This article delves into the two primary approaches: self-custody and third-party services, providing a comprehensive comparison to help you make informed decisions about securing your crypto holdings.
What Is Crypto Custody?
Credit from WallStreetMojo
Crypto custody involves the management and protection of private keys, which are essential for accessing and controlling cryptocurrencies. Without proper custody, digital assets are vulnerable to theft, loss, or unauthorized access. The two main types of crypto custody are:
- Self-Custody: Individuals or organizations manage their own private keys, retaining full control over their assets.
- Third-Party Custody: A trusted service provider manages the private keys on behalf of the user, offering convenience and additional security measures.tastycrypto
Self-Custody: Full Control with Increased Responsibility

Credit from tastycrypto
Self-custody offers the advantage of complete control over your digital assets. By managing your own private keys, you eliminate reliance on third parties, reducing exposure to risks such as platform hacks or insolvency. This approach is particularly appealing to those who prioritize privacy and autonomy in their financial dealings.Onramp Bitcoin
Advantages of Self-Custody
- Complete Control: You have sole authority over your assets, with no intermediary involved.tetratrust.com
- Enhanced Privacy: Transactions are conducted directly on the blockchain, offering greater anonymity.Kraken
- Reduced Counterparty Risk: Eliminates the risk of platform failures or regulatory actions affecting access to your funds.Kraken
Challenges of Self-Custody
- Security Risks: If you lose access to your private keys or recovery phrases, your assets are irretrievable.Kraken+1
- Technical Complexity: Managing private keys requires a certain level of technical knowledge and diligence.Kraken
- No Recovery Options: Unlike third-party services, there are no customer support channels to assist in case of issues.
Third-Party Custody: Convenience with Shared Control
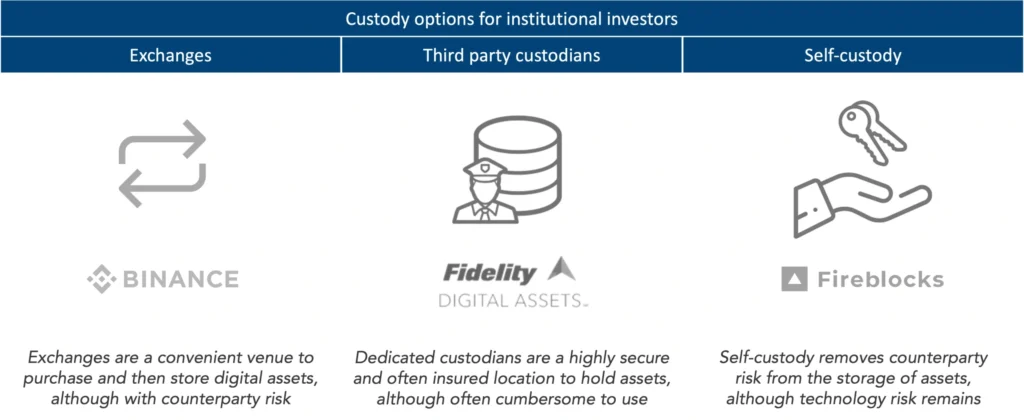
Credit from CMCC Global
Third-party custody involves entrusting your private keys to a service provider, such as a cryptocurrency exchange or a specialized custodian. These providers implement robust security measures, including insurance policies and regulatory compliance, to protect your assets.
Benefits of Third-Party Custody
- User-Friendly: Platforms often offer intuitive interfaces and customer support, simplifying the management of your assets.
- Advanced Security Features: Providers implement multi-signature wallets, insurance coverage, and regulatory oversight to enhance security.
- Recovery Options: In case of lost access, service providers typically offer recovery procedures to regain control of your assets.
Drawbacks of Third-Party Custody
- Counterparty Risk: Your assets are susceptible to risks associated with the service provider, such as hacking incidents or financial instability.
- Limited Control: You may face restrictions on withdrawals or account access, depending on the provider’s policies.
- Privacy Concerns: Transactions may require personal information, potentially compromising anonymity.
Comparing Self-Custody and Third-Party Custody
| Feature | Self-Custody | Third-Party Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over assets | Control shared with service provider |
| Security | Dependent on personal measures | Enhanced by provider’s security protocols |
| Privacy | Higher due to direct transactions | Potentially lower due to data requirements |
| Recovery Options | None | Available through provider |
| Technical Skill | Required | Minimal |
| Counterparty Risk | None | Present due to reliance on provider |
Best Practices for Crypto Custody
Regardless of the custody method chosen, implementing best practices can significantly enhance the security of your digital assets:
- Use Hardware Wallets: For self-custody, hardware wallets provide offline storage, reducing exposure to online threats.Investopedia+2New York Post+2
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For third-party services, 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Regular Backups: Maintain encrypted backups of your private keys and recovery phrases in secure locations.Brave+1
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of security developments and potential vulnerabilities in the crypto space.
Conclusion: Crypto Custody Explained

Credit from CCN.com
Understanding crypto custody is essential for safeguarding your digital assets. Both self-custody and third-party services offer distinct advantages and challenges. Your choice should align with your technical expertise, risk tolerance, and the level of control you wish to maintain over your assets. By adhering to best practices and staying informed, you can enhance the security of your cryptocurrency holdings and navigate the complexities of the digital asset landscape with confidence.




