Blockchain Nodes Made Simple: How They Keep Crypto Running
Introduction
In the world of cryptocurrency, Blockchain Nodes for Beginners are fundamental yet often overlooked components. These nodes are the decentralized computers that uphold the integrity, security, and operational continuity of blockchain networks. Understanding their role is crucial for anyone interested in how cryptocurrencies function beyond the surface level.
Section 1: What Are Blockchain Nodes?
Credit from Transak
A blockchain node is any device that participates in a blockchain network by running its protocol software and connecting to other nodes. These nodes serve as the infrastructure of the blockchain, ensuring that all participants have access to the same data and that the network operates smoothly .
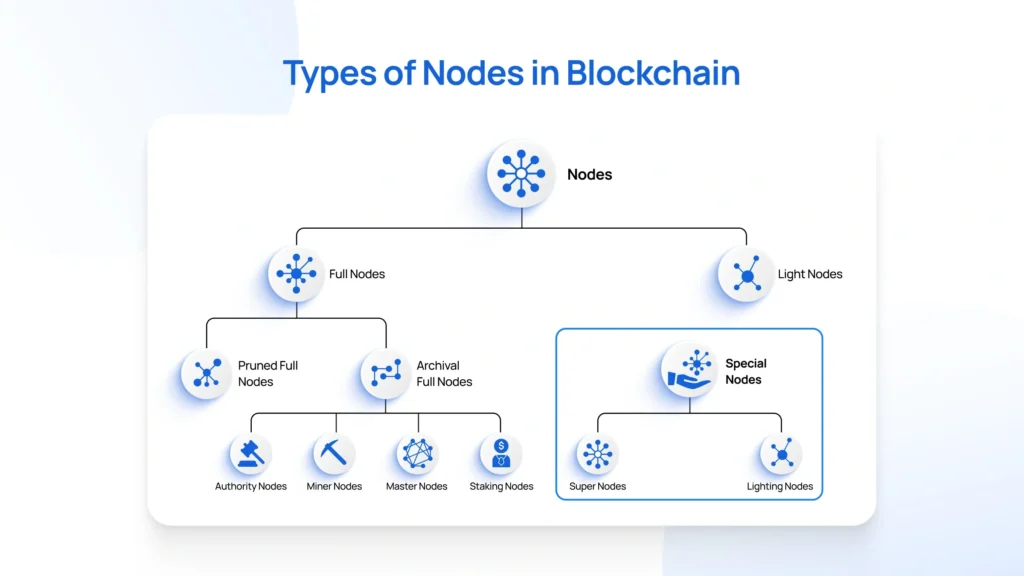
Types of Blockchain Nodes
- Full Nodes: These nodes store the entire history of the blockchain and validate all transactions and blocks. They are essential for maintaining the network’s integrity.
- Light Nodes (SPV Nodes): These nodes store only a subset of the blockchain data, relying on full nodes for transaction verification. They are less resource-intensive and suitable for devices with limited storage.
- Miner Nodes: In Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains, these nodes compete to solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the blockchain, earning rewards in the process.
- Validator Nodes: In Proof of Stake (PoS) systems, validators are chosen to propose and validate new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Section 2: How Blockchain Nodes Work
Credit from LinkRiver Blog
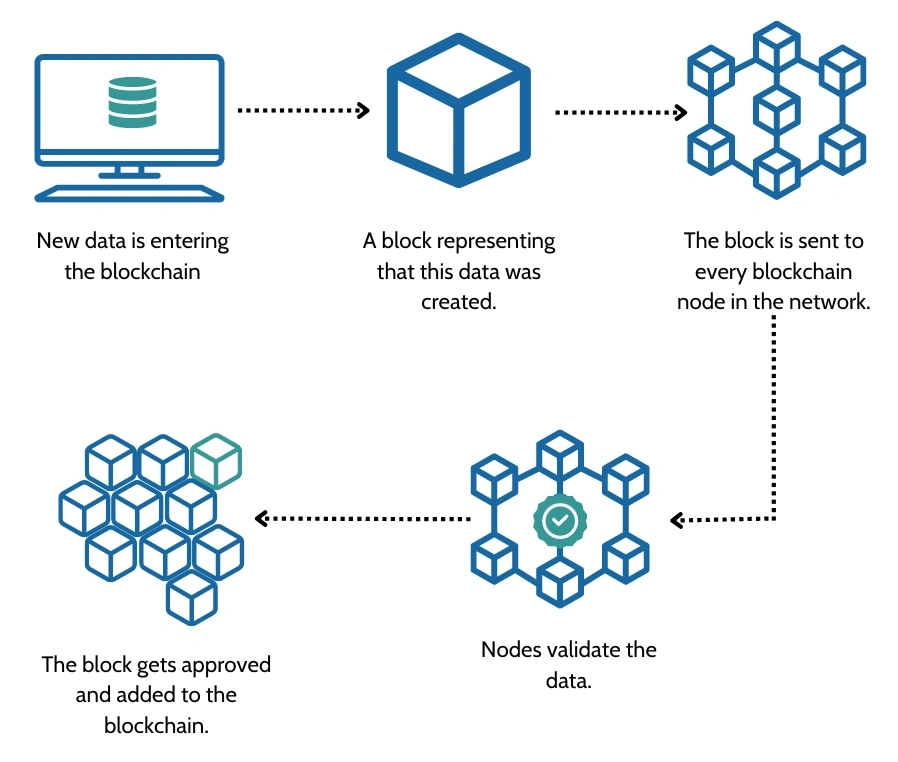
Blockchain nodes perform several critical functions to ensure the network operates correctly:
- Transaction Validation: Nodes verify the legitimacy of transactions by checking signatures, ensuring that the sender has sufficient balance, and confirming that the transaction adheres to the network’s rules.
- Block Validation: Before adding a new block to the blockchain, nodes check that it follows the consensus rules and contains valid transactions.
- Data Propagation: Nodes share information about new transactions and blocks with other nodes, ensuring that all participants are updated and synchronized.
- Consensus Participation: Nodes participate in the consensus mechanism (e.g., PoW or PoS) to agree on the state of the blockchain and the validity of new blocks.
Section 3: Why Blockchain Nodes Are Essential
Without nodes, a blockchain cannot function. They provide several key benefits:
- Decentralization: By distributing the network across numerous nodes, blockchains avoid single points of failure and reduce the risk of censorship or control by a central authority.
- Security: Nodes help protect the network from attacks by validating transactions and blocks, making it difficult for malicious actors to alter the blockchain’s history.
- Transparency: Since all nodes have access to the same data, they ensure that transactions are transparent and verifiable by all participants.
- Incentives: Many blockchain networks offer rewards to nodes for their participation, such as transaction fees or newly minted cryptocurrency, encouraging individuals to run nodes.
Section 4: Running a Blockchain Node
In Blockchain Nodes for Beginners, setting up a blockchain node can be an empowering way to participate in a network. Here’s a general overview of the process:
- Choose a Blockchain Network: Select a blockchain that aligns with your interests and goals, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Solana.
- Prepare Hardware: Ensure you have a computer with sufficient storage, processing power, and internet connectivity. Requirements vary by network.
- Install Node Software: Download and install the official software for the chosen blockchain. Follow the setup instructions provided by the network’s documentation.
- Sync with the Network: Allow your node to download the blockchain’s history and synchronize with other nodes. This process can take time, depending on the network’s size.
- Maintain the Node: Regularly update the node software, monitor its performance, and ensure it remains online to contribute to the network’s health.
Section 5: Nodes and the Future of Cryptocurrency
As blockchain technology evolves, the role of nodes continues to be pivotal:
- Scalability Solutions: Innovations like sharding and layer-2 solutions aim to improve blockchain scalability, and nodes will play a crucial role in implementing and supporting these advancements.
- Increased Participation: Efforts to make running a node more accessible, such as lighter node software and improved user interfaces, encourage broader community involvement.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Transitioning to energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Stake, reduces the environmental impact of running nodes, making participation more sustainable.
Conclusion
Blockchain nodes are the unsung heroes of the cryptocurrency world. They ensure that transactions are validated, data is secure, and the network remains decentralized. For beginners, understanding the role of nodes is the first step toward deeper engagement with blockchain technology. Whether you’re interested in running your own node or simply wish to grasp how cryptocurrencies function, recognizing the importance of nodes is essential.